
Exploring AI Agents: Models, Tools, and Frameworks for Development
An overview of Artificial Intelligence Agents, exploring current models, essential tools, and frameworks for building your own intelligent agents.
Diving into AI Agents: Models, Tools, and Frameworks
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly evolving, and one of the most exciting frontiers is the development of AI Agents. These autonomous entities are designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. From simple chatbots to complex robotic systems, AI agents are transforming how we interact with technology and solve problems.
This post will explore the current landscape of AI agents, focusing on available models, essential tools, and frameworks that empower developers to create their own intelligent agents.
What are AI Agents?
At their core, AI agents are software entities capable of intelligent behavior. They exhibit key characteristics such as:
- Autonomy: Agents operate without direct human intervention, making decisions independently.
- Reactivity: They perceive their environment and respond to changes in a timely manner.
- Proactiveness: Agents are goal-directed, taking initiative to achieve their objectives.
- Social Ability: Agents can interact with other agents and humans, collaborating and communicating as needed.
Models Powering AI Agents
Several models are driving the capabilities of modern AI agents. Here are some prominent examples:
1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
![]()
LLMs, like GPT-4, Bard, and Llama 2, are revolutionizing agent development. They provide:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Enabling agents to understand and interpret human language.
- Natural Language Generation (NLG): Allowing agents to communicate effectively in natural language.
- Reasoning and Planning: LLMs can be prompted to perform complex reasoning tasks and develop action plans.
- Examples:
- Conversational Agents: Chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer service bots.
- Content Creation Agents: Agents that can write articles, generate code, and create marketing copy.
- Personalized Learning Agents: Tutors and educational tools that adapt to individual student needs.
2. Reinforcement Learning (RL) Models
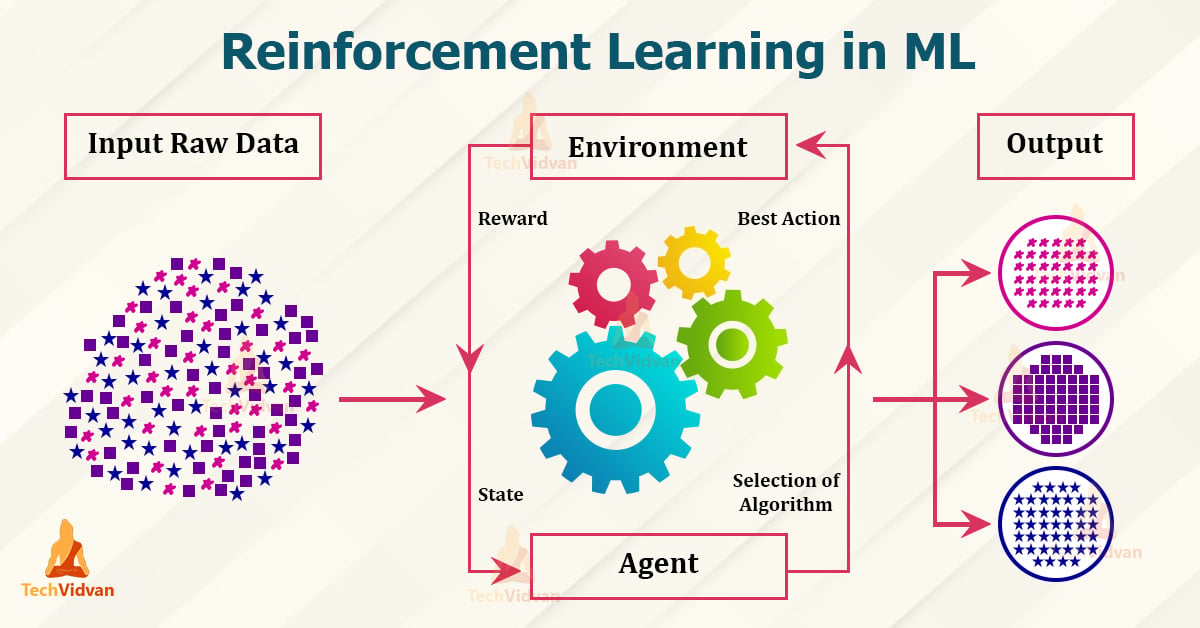
RL models enable agents to learn through trial and error, optimizing their actions based on rewards or penalties received from the environment.
- Adaptive Learning: Agents can learn complex strategies and policies by interacting with their environment.
- Optimal Decision Making: RL agents aim to maximize cumulative rewards, leading to efficient and goal-oriented behavior.
- Examples:
- Robotics and Automation: Training robots to perform tasks in dynamic and uncertain environments.
- Game Playing Agents: Developing agents that can master complex games like Go or chess.
- Resource Management Agents: Optimizing resource allocation in systems like energy grids or traffic networks.
3. Hybrid Models
Combining different AI models can lead to more robust and versatile agents. For instance:
- LLMs + RL: Integrating language understanding and generation from LLMs with the decision-making capabilities of RL creates powerful agents that can reason, plan, and interact effectively with humans and environments.
- Knowledge Graphs + LLMs: Using knowledge graphs to provide structured knowledge to LLMs enhances their reasoning abilities and reduces hallucinations.
- Examples:
- Autonomous Driving Agents: Combining perception models, planning algorithms, and decision-making modules.
- Personalized Recommendation Agents: Integrating user behavior models, content understanding, and collaborative filtering techniques.
Tools and Frameworks for Building AI Agents
Developing AI agents requires specialized tools and frameworks. Here are some key categories:
1. Agent Frameworks
These frameworks provide architectural blueprints and libraries to structure and build AI agents:
- LangChain (
python agent_example.py):from langchain.agents import initialize_agentfrom langchain.llms import OpenAIfrom langchain.agents import AgentTypellm = OpenAI(temperature=0)agent = initialize_agent(tools=[],llm=llm,agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,verbose=True)agent.run("What is the capital of France?")- A powerful framework for building agents using LLMs.
- Provides tools for connecting LLMs to various data sources and environments.
- Supports different agent types and memory mechanisms.
- AutoGen (
python autogen_example.py):from autogen import AssistantAgent, UserProxyAgent, config_list_from_jsonconfig_list = config_list_from_json(env_or_file="OAI_CONFIG_LIST")assistant = AssistantAgent("assistant", llm_config={"config_list": config_list})user_proxy = UserProxyAgent("user_proxy", code_execution_config={"work_dir": "coding"})user_proxy.initiate_chat(assistant, message="Plot a chart of NVDA and TESLA stock price change in the last 5 years.")- Focuses on building multi-agent systems and conversational AI applications.
- Enables complex workflows with interactions between multiple agents.
- Supports various communication patterns and agent roles.
- Mesa (
python mesa_example.py):from mesa import Agent, Modelfrom mesa.space import MultiGridfrom mesa.time import RandomActivationclass SimpleAgent(Agent):def __init__(self, unique_id, model):super().__init__(unique_id, model)def step(self):print(f"Agent {self.unique_id} is taking a step")class SimpleModel(Model):def __init__(self, N):self.num_agents = Nself.grid = MultiGrid(10, 10, True)self.schedule = RandomActivation(self)for i in range(self.num_agents):a = SimpleAgent(i, self)self.schedule.add(a)self.grid.place_agent(a, (1, 1))def step(self):self.schedule.step()if __name__ == '__main__':model = SimpleModel(10)for _ in range(5):model.step()- A framework for agent-based modeling, simulating complex systems with interacting agents.
- Useful for research and development of decentralized and emergent AI systems.
- Provides tools for visualization and analysis of agent behavior.
2. Development Tools
Essential tools for building and deploying AI agents:
- Python: The dominant programming language for AI development, with rich libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
- Cloud Platforms (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure): Provide infrastructure and services for training, deploying, and scaling AI agents.
- IDE (Integrated Development Environments): Tools like VS Code, PyCharm, and Jupyter Notebook facilitate coding, debugging, and experimentation.
- Version Control (Git): Essential for managing code changes and collaborating on agent development projects.
3. Datasets and Environments
High-quality datasets and simulation environments are crucial for training and evaluating AI agents:
- OpenAI Gym: A toolkit for developing and comparing reinforcement learning algorithms. Provides diverse environments from classic control problems to Atari games.
- DeepMind Lab: A 3D learning environment for agent-based AI research, focusing on complex navigation and problem-solving tasks.
- Kaggle Datasets: A vast repository of datasets for various AI tasks, including natural language processing, computer vision, and time-series analysis.
Final Thoughts
The field of AI agents is rapidly advancing, driven by breakthroughs in models, tools, and frameworks. As these technologies mature, we can expect to see AI agents play an increasingly important role in various aspects of our lives, from automating tasks to solving complex global challenges.
Conclusion
Building AI agents is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. By understanding the available models, leveraging powerful tools and frameworks, and continuously learning, you can contribute to shaping the future of intelligent and autonomous systems.
If you are passionate about artificial intelligence, agent-based systems, and the future of technology, let's connect! ( ^-^)**(^0^ )
Thank you for reading! Your comments and feedback are always welcome. ╰(°▽°)╯